Our planet is teeming with a stunning variety of creatures, big and small. But with so much life, conflicts and problems naturally arise. From everyday annoyances to life-threatening situations, animals face their share of challenges. What’s truly fascinating is the ingenuity—and sometimes sheer oddity—of the solutions humans devise. Get ready to explore some of the most peculiar animal predicaments and the even stranger ways we’ve tried to solve them!
10. Pig Perfume For Barking Dogs
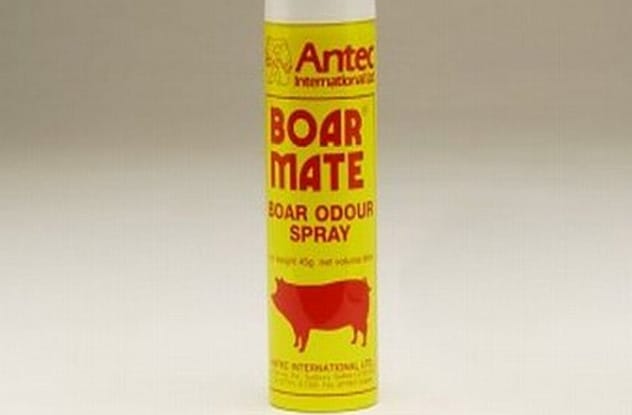

Ever been driven mad by a dog that just won’t stop barking? Scientist John McGlone faced this exact problem with his Cairn terrier. His solution wasn’t another training manual, but a trip to the lab. He concocted a spray called “Boar Mate” or “Stop That,” with a very special ingredient: pig pheromones.
This pheromone, androstenone, is produced by male pigs to attract sows. While female pigs find it irresistible, dogs apparently find it utterly repulsive. McGlone’s tests showed that a spritz of this pig-powered perfume in a dog’s face effectively silences them. It’s harmless, causing no adverse effects on their heart rate, just a moment of disorientation. Though the quieting effect lasts only about a minute, it offers a humane alternative to shock collars and could potentially reduce the number of dogs surrendered to shelters due to behavioral issues like excessive barking.
9. Glow-in-the-Dark Reindeer
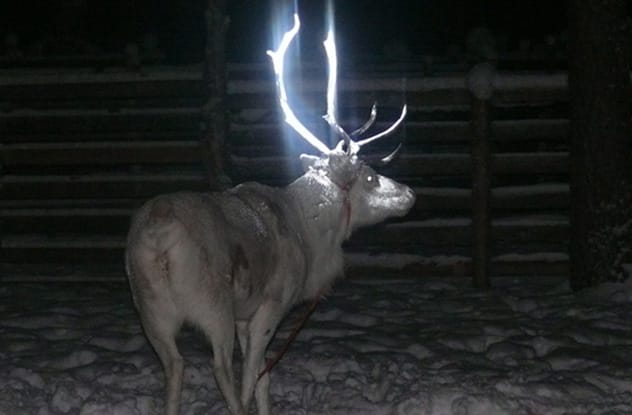

In the snowy expanse of Finnish Lapland, home to the famous Rovaniemi Santa Claus Village, reindeer are a common sight. Unfortunately, unlike Santa’s magical team, these reindeer can’t fly, making them vulnerable to road accidents, especially at night. Thousands die each year in collisions with vehicles.
To tackle this, reindeer breeders came up with a luminous idea. In 2014, they began experimenting by coating the fur and antlers of about 20 reindeer with two types of reflective paint. One paint, for the fur, is designed to wash off eventually, while the antler paint is more permanent. The goal is to make the reindeer highly visible in car headlights, preventing tragic accidents. If successful, Lapland might soon feature herds of caribou glowing eerily in the dark, safeguarding both animal and driver.
8. The Mongoose Misunderstanding & Vicks VapoRub Fix
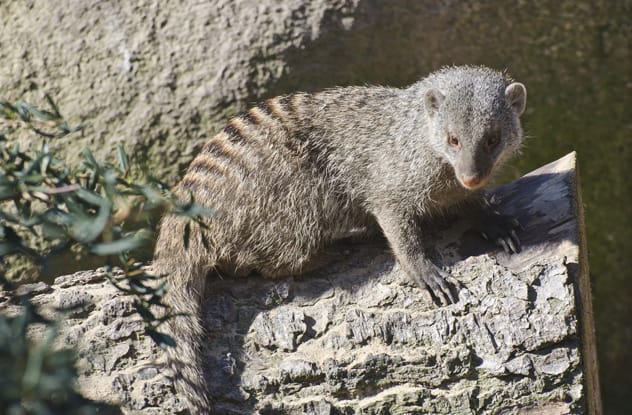

The Fort Wayne Children’s Zoo in Indiana once faced a peculiar social drama within their banded mongoose exhibit. After a mongoose named Rikki returned from a routine vet checkup, his group mates began to shun and even bully him. The zookeepers were baffled by this sudden change in behavior.
It turns out, banded mongooses heavily rely on scent to identify each other. The vet visit had altered Rikki’s natural smell, making him an unrecognizable stranger to his own family. Zookeeper Nancee Hutchinson couldn’t restore Rikki’s old scent, but she could make everyone smell equally…unusual. She smeared Vicks VapoRub in their enclosure, allowing all the mongooses to roll in it. With everyone smelling strongly of menthol, Rikki was no longer an olfactory outsider and was welcomed back into the fold.
7. Men in Monkey Masks vs. Macaque Mayhem

New Delhi has long struggled with a rhesus macaque problem. These primates, emboldened by food handouts, have become a nuisance, invading government buildings, homes, and even causing fatalities. In a desperate attempt, the city initially hired langur monkeys, natural enemies of macaques, to scare them off. However, this plan was shut down due to animal rights concerns for the langurs.
Not ready to abandon the monkey-vs-monkey strategy entirely, the city council adopted a more theatrical approach. They hired 40 men to dress up in langur monkey costumes. These “very talented” individuals don masks and suits, hide behind trees, and mimic langur calls to frighten the macaques away from urban areas. It’s a comical sight, but officials hope it’s a step towards peacefully resolving their primate predicament.
6. An Interstellar Sperm Bank for Endangered Species
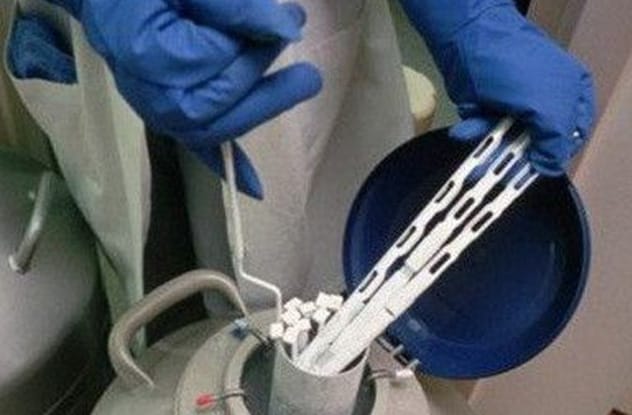
With hundreds, possibly thousands, of species vanishing each year, scientists are racing against time to preserve biodiversity. Researchers at Kyoto University, led by Takehito Kaneko, have pioneered a novel method for preserving the sperm of endangered animals. Traditionally, reproductive cells are stored in liquid nitrogen at extremely low temperatures.
The Kyoto team developed a technique to freeze-dry sperm from animals like chimpanzees, slow lorises, and giraffes using a special preservative. This allows the sperm to be stored at a much warmer 4 degrees Celsius (39 °F), saving energy and making it more resilient to power outages. Their ambitions are literally out of this world: they envision one day using these freeze-dried samples to populate other planets with Earth’s creatures, though they’re still working on perfecting egg preservation.
5. Human-Scented Cologne for Cows to Combat Malaria
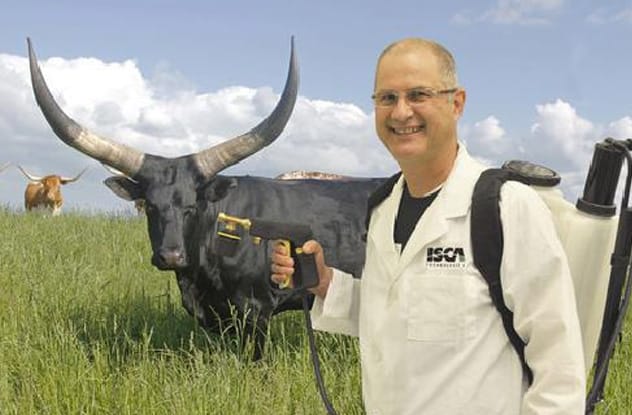

Mosquitoes are more than just annoying pests; they’re vectors for deadly diseases like malaria, which puts billions at risk globally. The Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation has invested significantly in fighting malaria, funding innovative solutions like mosquito-zapping lasers.
More recently, the foundation supported a smellier strategy by ISCA Technologies, a pest management company. Their idea? Develop a human-scented cologne for cows. Since cows can’t contract human malaria, the plan is to lure mosquitoes away from people and towards cattle treated with this special perfume. If the cattle are also treated with insecticide, any mosquito attempting to bite would be killed. This approach could protect humans while also benefiting cows by confusing other insects that typically prey on them – a win-win, unless you’re a mosquito.
4. Sharks on Twitter: A High-Tech Warning System
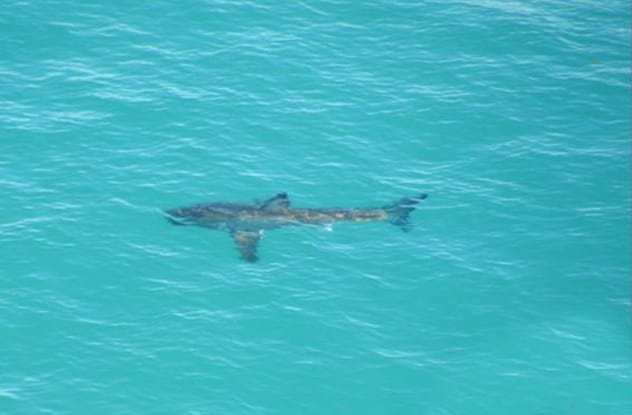

While shark attacks are rare, they do happen, and Australia has a particularly high rate of fatal encounters. Instead of controversial culling measures, government researchers in Western Australia have embraced social media for a creative solution. In 2013, they tagged over 300 sharks with transmitters.
These devices monitor the sharks’ locations. If a tagged shark ventures within 800 meters (about half a mile) of the shore, the transmitter sends an alert. This alert is then automatically posted to the Surf Life Saving Western Australia Twitter feed, providing real-time warnings to beachgoers and surfers. While it doesn’t cover every shark in the ocean, it’s an innovative use of technology to enhance public safety and keep social media feeds exciting.
3. The Beehive Fence: A Stinging Deterrent for Elephants
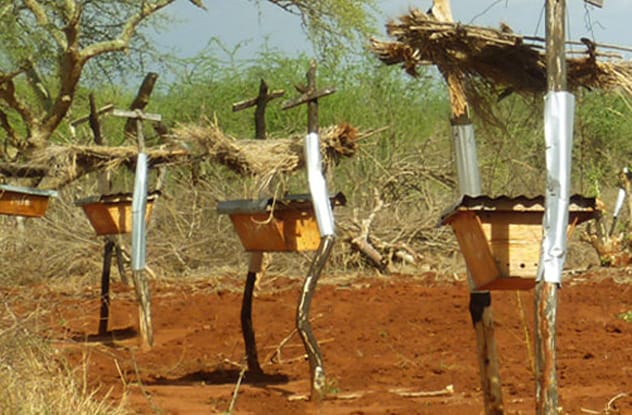

It’s a myth that elephants are scared of mice, but they are genuinely terrified of bees. An elephant’s thick skin offers a lot of protection, but their eyes and trunks are extremely sensitive to bee stings. This fear has become the basis for an ingenious solution to human-elephant conflict in Africa.
As human populations expand into elephant habitats in Kenya, crop-raiding by hungry elephants has become a serious issue, sometimes leading to dangerous confrontations. Researchers from Save the Elephants developed the “beehive fence.” These fences consist of beehives suspended from poles and connected by a wire. If an elephant tries to cross by disturbing the wire, the hives swing, agitating the bees, which then swarm out. This is usually enough to send the elephants retreating, protecting crops and reducing casualties on both sides. As a sweet bonus, farmers can harvest and sell the honey.
2. Slower Speeds to Save Dragonflies
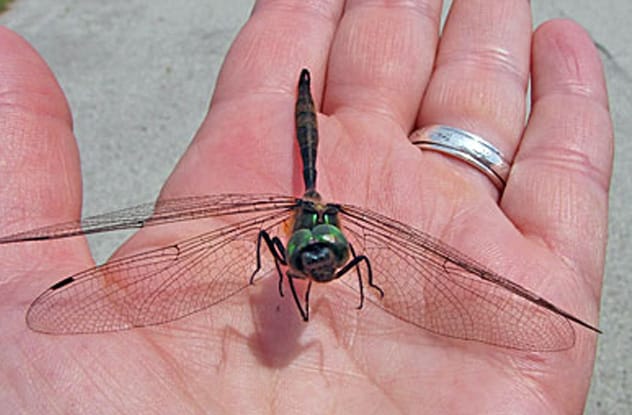

The Hine’s emerald dragonfly is an endangered species with a shrinking habitat, now mostly found in parts of Wisconsin like Door County. These dragonflies mature over five years and emerge as adults between June and August, which unfortunately coincides with peak tourist season and increased traffic.
Thousands of these rare dragonflies are killed each year by vehicles. Amber Furness, a graduate student from the University of South Dakota, studied this problem by driving at various speeds and observing the impact on dragonflies. Her research revealed a simple yet effective solution: if drivers reduce their speed to around 48 kilometers (30 miles) per hour, dragonflies are more likely to just bounce off windshields unharmed rather than being fatally struck. Door County officials have considered her proposal to lower speed limits during the summer, a small change that could make a big difference for these delicate flyers.
1. The Philosophical Plan to End All Animal Suffering

Nature is a realm of breathtaking beauty but also undeniable brutality. Predation, pain, and death are inherent parts of the natural world. However, British philosopher David Pearce proposes a radical, and perhaps the strangest, solution of all: to end animal suffering completely.
In his manifesto, “The Hedonistic Imperative,” Pearce outlines a vision that includes transitioning humanity to veganism via synthetic meat and, more controversially, eliminating predation from the planet. This could involve either making predators extinct through methods like immunocontraception or genetically reprogramming carnivores—from sharks to spiders—to crave salads instead of flesh. Herbivores too would need reconditioning to trust their former enemies. Pearce argues that because animals experience pleasure and pain, and none wish to suffer, intelligent beings have a duty to eliminate this suffering. It’s a profound, and deeply divisive, idea that questions the very nature of the wild world as we know it.
These fascinating, and sometimes startling, solutions show the lengths to which humans will go to address problems in the animal kingdom. From simple scent tricks to ambitious technological interventions, our relationship with wildlife is constantly evolving.
What do you think of these unusual solutions? Do you know of any other strange animal problem fixes? Leave your comment below!










