The Theory of Evolution, a cornerstone of modern biology, elegantly explains the evolution of species through natural selection. While widely accepted within the scientific community, it often faces opposition, sometimes fueled by misunderstandings or conflicting beliefs. Since Darwin and Wallace’s groundbreaking work, numerous peculiar claims have surfaced, attempting to undermine the theory. Let’s explore ten of the most bizarre arguments leveled against evolution.
Evolution Is Just A Theory

In science, a theory isn’t a mere hunch. It’s a well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the natural world that incorporates facts, laws, inferences, and tested hypotheses. Think of the Theory of Gravity or the Theory of Planetary Motion. These aren’t casual guesses; they’re comprehensive frameworks built upon years of meticulous observation and experimentation.
A scientific theory’s strength lies in its adaptability. It’s not immutable. New evidence can refine or even reshape it. The modern Theory of Evolution integrates discoveries impossible in Darwin’s time, such as DNA and cellular biology. Dismissing evolution as “just a theory” misunderstands the very nature of scientific inquiry.
The Fossil Record Is Incomplete
Fossilization is an incredibly rare event. For an organism to become a fossil, it needs to be in the right place, at the right time, under very specific conditions. Most organisms decompose, leaving no trace. The fossil record, while extensive, represents a tiny fraction of all life that has ever existed.
The rarity of fossils means there will always be gaps in the record. However, these gaps don’t invalidate the theory of evolution. Instead, each new fossil discovery provides additional insights, filling in pieces of the puzzle and raising new questions. As the animated series Futurama cleverly pointed out, finding a missing link often creates two new gaps.
It Relies Too Heavily On Chance Making It Mathematically Impossible

This argument often claims that the probability of complex life arising from random mutations is infinitesimally small. Critics point to the supposed impossibility of a single-celled organism evolving into humans through purely random processes. This argument often stems from a misunderstanding of how natural selection actually works.
Evolution isn’t purely random. While mutations occur randomly, natural selection acts as a filter, preserving beneficial mutations and weeding out harmful ones. This non-random process dramatically increases the likelihood of adaptation and the development of complex traits over vast stretches of time.
Evolution Has Never Been Observed
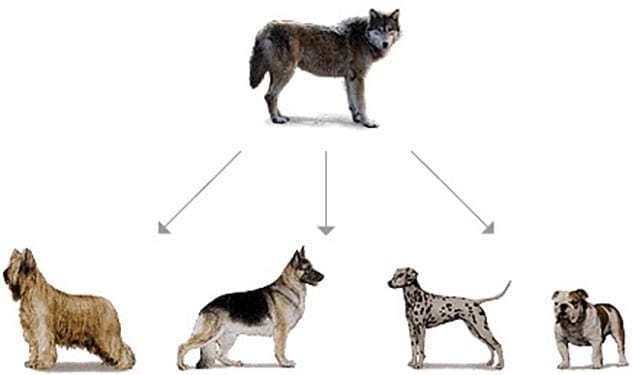
This argument often stems from a misunderstanding of the timescales involved. Macroevolution, the evolution of new species, typically occurs over long periods and can be difficult to observe directly. However, microevolution, changes within a species, is readily observable.
A classic example is the evolution of pesticide resistance in insects. As insects with genes for resistance survive and reproduce, they pass on those genes to future generations. Over time, the entire population becomes resistant to the pesticide, demonstrating evolution in action.
It Defies The Second Law Of Thermodynamics

The Second Law of Thermodynamics states that the entropy (disorder) of an isolated system always increases over time. Critics argue that evolution, which creates complexity and order, violates this law. This argument misapplies the Second Law.
The Earth is not an isolated system. It receives a constant influx of energy from the sun. This energy allows for the creation of order and complexity, as seen in the growth of plants and the development of complex life forms. These processes don’t violate the Second Law because the overall entropy of the universe, including the sun, still increases.
Not All Scientists Support It So It Must Be False

While it’s true that not every single scientist on Earth accepts the Theory of Evolution, the overwhelming majority of biologists do. Scientific consensus doesn’t equate to absolute proof, but it does reflect the weight of evidence and expert opinion. The level of support for evolution within the relevant scientific community is exceptionally high.
In science, debates and disagreements are normal. However, the core principles of evolution are firmly established, supported by a vast body of evidence from diverse fields such as genetics, paleontology, and comparative anatomy.
Evolution Cannot Explain How Life First Appeared On Earth

Evolution explains how life changes over time, not how life originated. The origin of life, known as abiogenesis, is a separate field of study that explores how life may have arisen from non-living matter. Conflating these two distinct areas is a common error.
Even if scientists were to definitively prove that life originated through some extraterrestrial or supernatural means, it wouldn’t negate the overwhelming evidence for evolution. Evolution explains what happened after life arose, regardless of its initial origin.
If Humans Evolved From Monkeys Then Why Are There Still Monkeys?

Humans didn’t evolve from monkeys. Humans and monkeys share a common ancestor that lived millions of years ago. Evolution is not a linear progression; it’s more like a branching tree. Different populations can evolve in different directions, leading to the diversity of life we see today.
Humans are hominids, belonging to the group of great apes. Monkeys are simians, sharing a more distant common ancestor with humans. The persistence of monkeys doesn’t disprove evolution any more than the existence of cousins disproves your direct lineage.
The Banana Argument
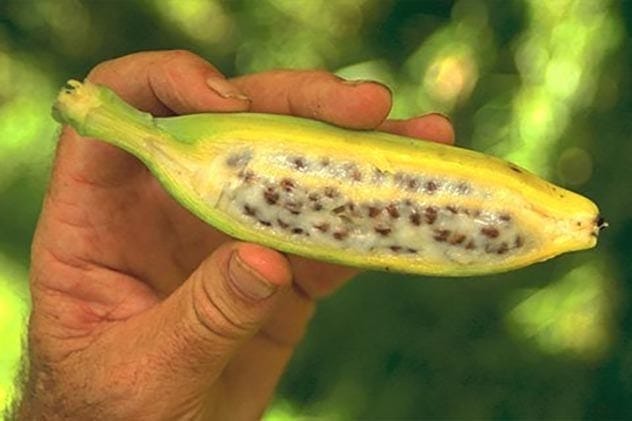

This argument, popularized by creationist Ray Comfort, claims that the banana is perfectly designed for human consumption, thus proving intelligent design. Comfort argued that the banana’s shape, peel, and easy-to-open tab are evidence of divine creation. The problem? Modern bananas are the result of extensive artificial selection by humans.
Wild bananas are small, seedy, and unpalatable. The bananas we eat today are the product of cross-pollination and genetic manipulation. Far from disproving evolution, the banana is a testament to the power of artificial selection, a form of evolution driven by human intervention.
The Crocoduck

Creationists Kirk Cameron and Ray Comfort famously presented the “crocoduck” as an example of a missing transitional fossil. They argued that if evolution were true, we should find creatures with features of both crocodiles and ducks. The absence of such a creature, they claimed, disproved evolution. Ironically, paleontologists later discovered Anatosuchus, an ancient crocodile with a broad, flat snout resembling a duck’s bill.
While not a perfect “crocoduck,” Anatosuchus demonstrates that evolution can produce surprising combinations of traits. The “crocoduck” argument, intended to ridicule evolution, inadvertently highlighted the creativity and adaptability of natural selection.
In Conclusion
The theory of evolution is a robust and well-supported scientific explanation for the diversity of life on Earth. While criticisms and alternative viewpoints exist, they often stem from misunderstandings of the theory itself or a lack of familiarity with the vast body of evidence that supports it. From the nature of scientific theories to the interpretation of the fossil record, understanding the nuances of evolution is crucial for informed discussions and a deeper appreciation of the natural world.
What do you think about these claims? Leave your comment below!