Science continues to push the boundaries of what’s possible, offering innovative solutions to global challenges and improving our daily lives. From fighting pandemics to understanding the complexities of the human brain, scientists are tirelessly working toward a brighter future. Let’s explore some of the most promising scientific advances that may soon change the world as we know it.
mRNA Vaccines
While DNA holds the genetic instructions in our cells, mRNA plays a crucial role in protein synthesis. Cells create mRNA copies from DNA to guide protein production; these copies are discarded if damaged. Scientists have harnessed mRNA to develop a new type of vaccine. Unlike traditional vaccines that use weakened or inactivated viruses, mRNA vaccines deliver a small piece of mRNA that teaches our cells to produce a viral protein. This triggers an immune response, creating antibodies without ever exposing us to the actual virus.
The Moderna vaccine for COVID-19 uses mRNA to instruct cells to make the spike protein found on the virus’s surface. This simplifies vaccine development, drastically reducing the time from planning to clinical trials. This innovative approach holds immense promise for দ্রুত responding to future pandemics.
Mind-Controlled Prostheses
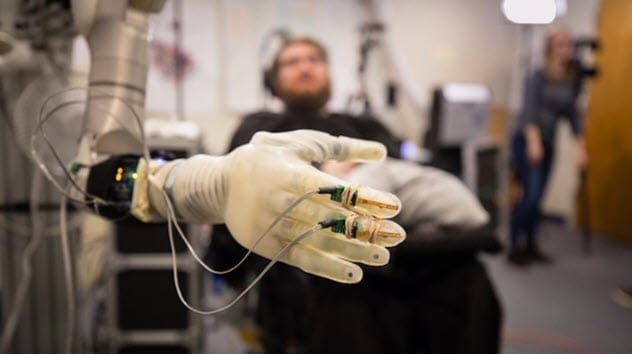
Imagine controlling a prosthetic limb with your thoughts. In 2016, researchers at the University of Pittsburgh, UPMC, and the University of Chicago achieved this milestone. Nathan Copeland, paralyzed from the chest down, regained the ability to feel and control a prosthetic limb using only his mind.
Electrodes implanted in Copeland’s brain interpret his intentions to move the robotic arm. Sensors in the prosthetic hand send electrical signals back to his brain, allowing him to feel touch. This groundbreaking technology offers hope for those with paralysis or limb loss, potentially restoring lost function and improving quality of life. Further research is underway, supported by a $7 million grant from the National Institutes of Health.
Understanding Autism
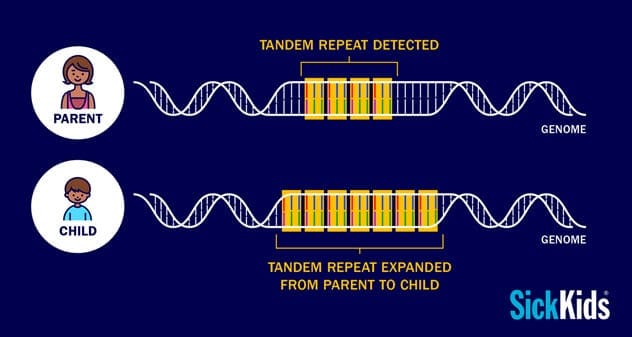
Autism, a complex and often misunderstood disorder, affects social and verbal communication and can cause repetitive behaviors. Scientists at the Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto have made a significant discovery by analyzing the DNA of autistic children and their parents. They found that autistic children often have a higher number of tandem repeats, which are repeated DNA sequences, in genes related to brain function.
These expanded tandem repeats can impair gene function, contributing to the development of autism. Identifying this genetic marker could lead to earlier diagnosis and a better understanding of the causes of autism, potentially paving the way for new treatments and therapies. Researchers believe similar tandem repeat expansions may also be linked to epilepsy and schizophrenia.
A Treatment For Alzheimer’s Disease

Alzheimer’s disease, a devastating neurodegenerative condition, disrupts brain function due to tangled tau proteins and beta-amyloid plaques. NeuroEM Therapeutics, Inc., has developed a wearable cap, the MemorEM, that emits electromagnetic waves to break down these protein buildups.
Early clinical studies showed that some patients experienced a return of cognitive function after using the cap. Independent labs have replicated these results in mice. While still in the early stages, this treatment offers a promising new approach to combatting Alzheimer’s, as current drug treatments provide limited relief. The potential to restore cognitive function represents a significant breakthrough in Alzheimer’s research.
Universal Flu Vaccines
Annual flu shots are necessary because flu virus strains mutate rapidly. Current vaccines target the head of the HA protein, which changes frequently. However, the HA protein’s stem remains relatively constant across different strains.
NIAID’s Vaccine Research Center has developed a universal flu vaccine targeting this stem. This could provide long-lasting immunity against multiple flu strains with a single shot. Clinical testing is underway, and if successful, this vaccine could revolutionize flu prevention, eliminating the need for annual vaccinations.
The Medusavirus Discovery
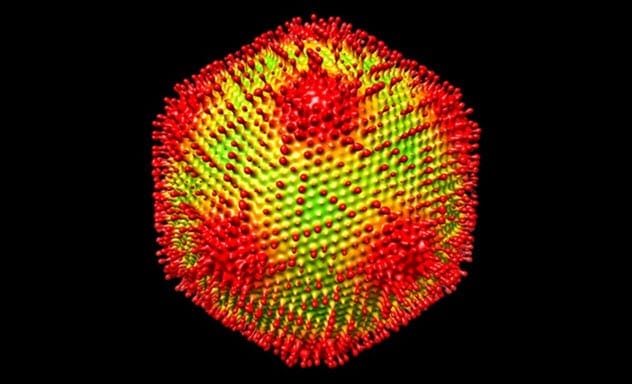
The Medusavirus, found in a Japanese hot spring, turns its amoeba hosts into stone, reminiscent of the mythical Medusa. While harmless to humans, this virus contains histones, proteins typically found in the nuclei of eukaryotic cells. Viruses, however, lack nuclei.
Scientists believe the Medusavirus could provide insights into the evolution of eukaryotic life. By studying how this virus acquired histone proteins, researchers may unlock clues about how early cells evolved into the complex cells found in our bodies today.
Metal-Eating Microbes
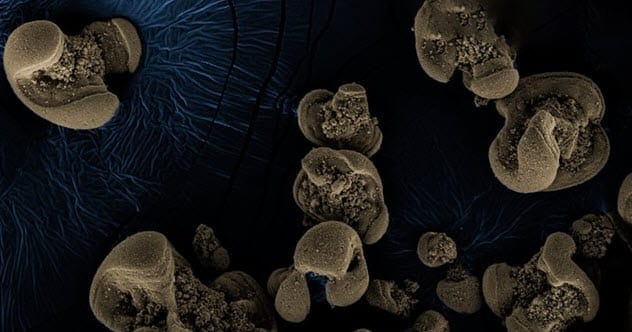
For years, the accumulation of manganese oxide on the seafloor and in water pipes puzzled scientists. Caltech scientist Jared Leadbeater accidentally discovered that microbes could be responsible when manganese carbonate in his lab turned into black manganese oxide.
Further research identified bacteria that consume electrons in manganese, leaving manganese oxide behind. This discovery marks the first time microbes have been found to use manganese as an energy source. This finding could reshape our understanding of how manganese shaped the planet’s evolution.
A Cure For Ebola

Ebola, a deadly viral illness, has been a major global health concern. In 2019, a clinical trial identified a new drug therapy that significantly reduced the death rate from 75% to 29%. If treated early, the death rate dropped to as low as 6%.
The drug, developed by Regeneron, contains a mixture of antibodies that specifically target the Ebola virus. This therapy is currently being tested and could become a lifesaving tool in combating future Ebola outbreaks, offering hope for a cure.
Science’s relentless pursuit of knowledge continues to produce extraordinary advancements, offering solutions to some of humanity’s most pressing challenges. Which of these scientific breakthroughs excites you the most? Leave your comment below and share your thoughts!










