Who doesn’t love animals? We all enjoy the charm of our furry and feathered friends, but their contributions go far beyond simple companionship. Animals are vital in numerous scientific fields, significantly advancing human life and solving everyday problems.
Scientists are constantly uncovering unique animal traits and applying them in innovative ways. From the intelligence of trainable mammals to the evolved chemical properties of lesser-known creatures, here are ten remarkable ways animals are helping us that you might not have realized.
Keyhole Limpet Proteins
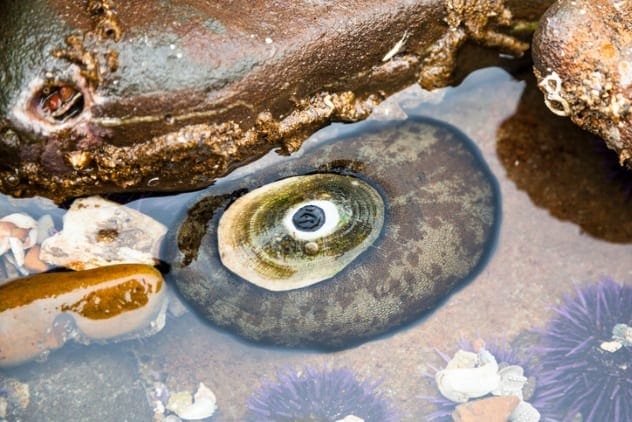

Keyhole limpets, sea snails with conical shells featuring a small hole at the top, possess a fascinating secret: keyhole limpet hemocyanin (KLH). This protein is used in medicines, including cancer and Alzheimer’s treatments, and in vaccines for both humans and animals.
The complex structure of hemocyanin, with its numerous binding sites, makes it ideal for fighting diseases. Companies are specializing in KLH production as its uses in medicine continue to expand. The fact that limpets are invertebrates also sidesteps ethical concerns about using animals with brains for scientific testing.
Cancer-Sniffing Dogs

Dogs, with their incredibly sensitive noses, have the remarkable ability to detect cancer. Canines possess about 60 times more sensory nerves in their noses than humans. Studies in the early 1990s demonstrated that trained dogs could accurately identify urine samples from cancer patients about 95 percent of the time, sniffing out liver, lung, and breast cancer.
While dogs may not become fixtures in doctor’s offices, their olfactory capabilities are inspiring new diagnostic tools. Scientists have developed devices that mimic a dog’s ability to “smell” chemicals linked to cancerous cells, showing promise for future cancer detection methods.
Diabetes Dogs

Stories of dogs detecting low blood sugar in diabetes patients have evolved from charming anecdotes to recognized facts. Scientists discovered that when blood sugar drops dangerously low, the amount of a chemical called isoprene nearly doubles in a patient’s exhaled breath. Humans can’t detect this change, but dogs can.
Trained diabetes alert dogs (DADs) can alert their owners to this change, giving them time to stabilize their glucose levels and prevent serious health episodes. Though expensive, these dogs can be lifesavers for people living with diabetes.
Airport Falconry
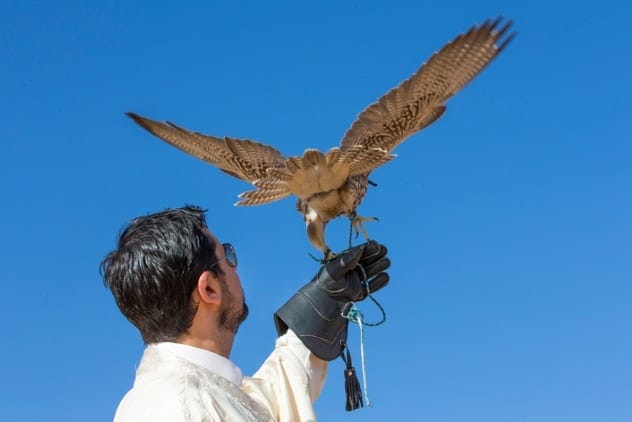

Remember the movie Sully? Birds flying into airplane engines pose real risks, leading to emergency landings and costly damage. Trained falcons offer a solution: they are used at airports to scare away smaller birds, preventing them from flying into planes during takeoff.
This practice is widespread in the United States, where bird strikes can cause over $500 million in damages annually. With the cost of a single damaged engine reaching up to $2 million, training falcons is a worthwhile investment for flight safety.
Growing Human Organs In Animals
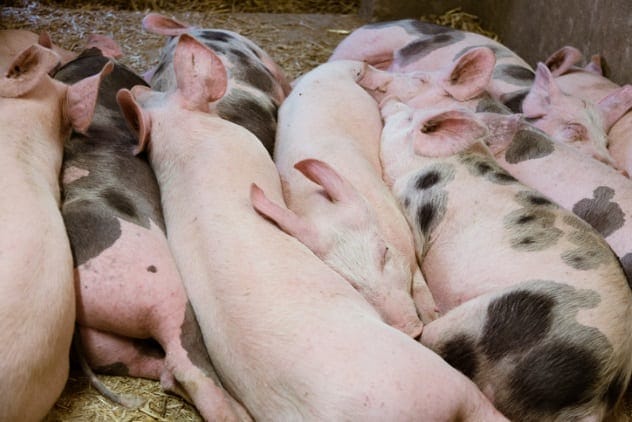

With tens of thousands of people awaiting organ transplants, scientists are exploring ways to grow healthy human organs independently. One promising approach involves growing human organs inside animals, such as pigs.
Stem cells from a transplant patient’s skin are introduced into an animal engineered to develop without a specific organ. This allows the stem cells to grow into the needed structure, offering a potential solution to the organ shortage. However, ethical concerns surrounding the use of animals in this way have led to bans on the procedure.
Cancer Immunity In Sharks
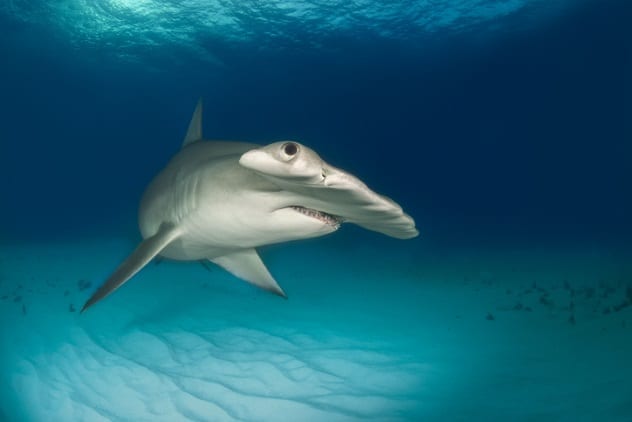

Sharks, often feared, possess remarkable immune systems that may hold the key to fighting cancer. Studies have shown that sharks have an increased immunity to cancer due to highly evolved immune systems. Species like hammerheads and great whites exhibit genes remarkably similar to those in humans.
Genes like “legumain” and “Bag1” play roles in apoptosis, or programmed cell death, a system that eliminates defective cells, including cancerous ones. Sharks also boast rapid healing rates and low infection rates, suggesting unique genetic factors that could benefit human medicine.
Dogs Sniffing For Science
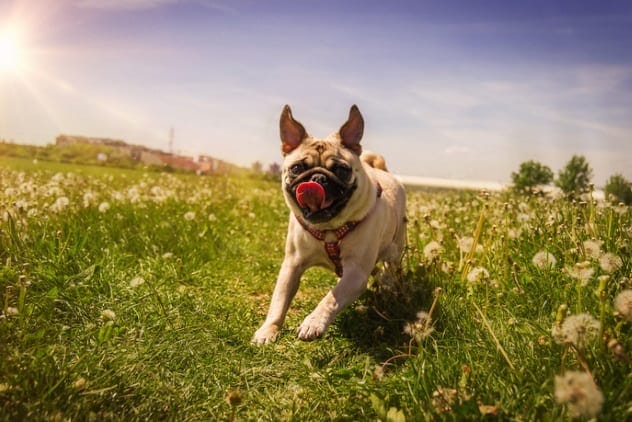

Beyond detecting diseases, dogs are helping scientists in conservation efforts. Specially trained dogs are used to track down invasive plant species, helping to keep natural environments safe and beautiful.
Imagine spending your days with a dog, training it to identify specific plant scents, and then letting it roam free in open fields. Teams of dogs can find twice as many invasive plants as humans, offering an effective and inexpensive method for conservational science.
Algae Used In Biofuels

Though not animals, algae offer powerful solutions as a source of renewable energy. With thousands of photosynthetic algae types, their ability to convert sunlight into energy can help address our energy crisis.
By extracting lipids from algae and subjecting them to hydrothermal liquefaction, the energy created by the algal cells can be concentrated for use in jet fuel, gasoline, and ethanol. Even big oil companies are taking notice of the potential of algae as a sustainable energy source.
Oysters Removing Nitrogen

ExxonMobil’s project to add one billion oysters to New York’s coastal ecosystem demonstrates the value of these mollusks. Oysters retain nitrogen in their systems, helping to maintain homeostasis and promote a healthier marine environment by reducing harmful algae blooms.
Oysters filter water with high nitrogen levels and convert nitrogen into less toxic forms. This natural process makes the water safer and healthier, showcasing the critical role of oysters in marine ecosystems.
Plastic-Devouring Worms
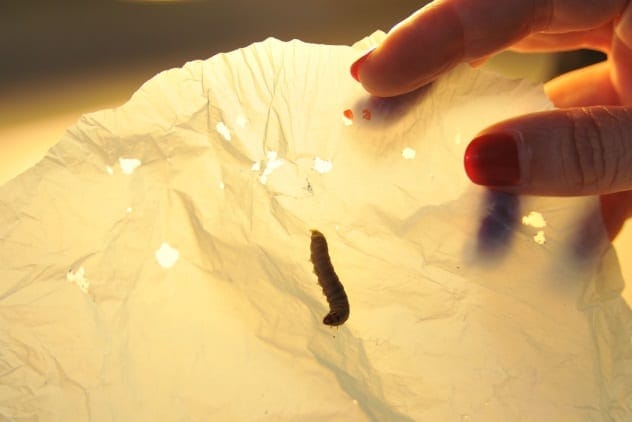

Plastic pollution is a global crisis, but wax moth larvae offer a glimmer of hope. These larvae, often used as fishing bait, can eat plastic without being harmed.
Scientists are studying these worms to determine their potential in lessening human waste. While it’s still unknown if they can thrive on plastic alone, wax moth larvae may soon be bred to help tackle our plastic pollution problems, offering a bizarre but promising solution.
Animals play far more significant roles in our lives than we often realize. From medical breakthroughs to environmental solutions, their contributions are invaluable. Which of these facts surprised you the most? Leave your comment below!