Believe it or not, we’re well into the 21st century, and the last two decades have brought remarkable changes. Among all the social and political shifts, medicine has seen some truly significant advancements. Let’s dive into the top 10 medical breakthroughs that have shaped the first part of this century.
Prosthetics Have Gone Bionic
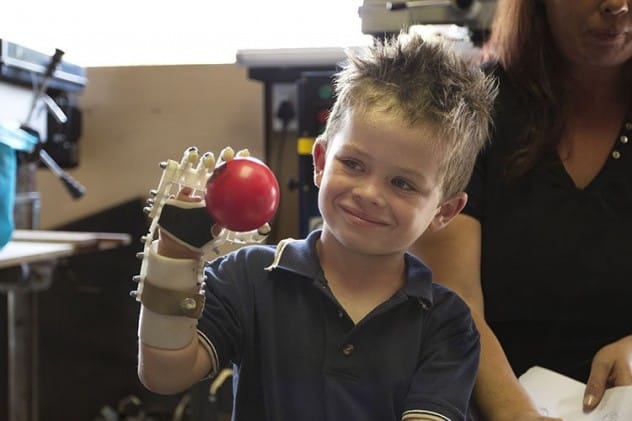
Remember the Six Million Dollar Man? What seemed like a far-off fantasy in the 1970s is now a reality. Bionic prosthetics have evolved from science fiction to tangible solutions, offering enhanced functionality. While we’re not turning astronauts into superheroes, modern prostheses allow users to manipulate them with their minds by reading electric signals. Electrodes placed on the skull enable individuals to open and close bionic hands, pick up objects, and even feel with bionic fingers. Bionic lenses are also restoring vision, and researchers are developing implantable neuroprosthetic devices to control computers. These advancements promise even greater improvements in the coming years.
HIV/AIDS Treatment Takes on the Virus
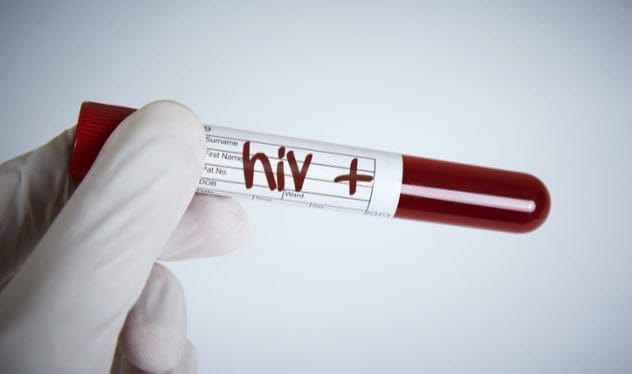
For many years, HIV seemed unbeatable. Infection invariably led to AIDS and, ultimately, death. The introduction of Atripla in 2006 marked a turning point by combining three antiretroviral drugs into a single dose. Later, in 2013, Stribild combined four medications into one. The release of Juluca and Dovato in 2017 and 2019 further revolutionized treatment options, offering effective single-dose therapies for nearly all HIV patients. These breakthroughs not only reduce the progression to AIDS but also significantly lower healthcare costs.
We Cracked The Human Genome
In 1990, the Human Genome Project embarked on deciphering the human genome by determining and mapping the base pairs that make up human DNA. By 2000, a rough draft was released, providing the first complete set of human genetic information. Three years later, the final draft mapped the three billion nucleotides in our DNA. This project has been instrumental in understanding human genetics, enabling easier and cheaper mapping of individual genomes. This allows for the identification of disease-causing mutations before they manifest, furthering cancer research, and revealing the genetic basis of nearly 5,000 conditions, a vast improvement from the mere 60 understood before the project.
Advances in Genetic Engineering

While science fiction often portrays genetic engineering as a source of monsters, the reality is far more promising. Genetic engineering, particularly CRISPR technology, offers ways to correct congenital defects and mutations that cause disease. CRISPR allows for targeted editing of an organism’s genes and can be used in agriculture, pest control, and the creation of genetically modified organisms. Awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2020, CRISPR has shown effectiveness in treating cancer, progeria, sickle cell disease, and many other genetically-linked conditions. As research advances, CRISPR is likely to become a common therapeutic tool.
Heart Disease Is No Longer A Death Sentence

Before the 21st century, treatment for heart attack patients was limited. Today, deaths from heart disease have decreased by 40%. Medications like Lipitor, Mevacor, and Crestor slow atherosclerosis, reducing the occurrence of heart attacks. When heart attacks do happen, rapid intervention is key. Genetically engineered tissue plasminogen activators (tPA) can dissolve clots, restoring blood flow. Improvements in surgical treatments and the American Heart Association’s goals to reduce cardiac deaths have contributed to far better outcomes for patients.
Stem Cell Research & Application Made Leaps & Bounds
Stem cell research isn’t new, but the 21st century has seen significant advancements in its application. Stem cells can divide into new stem cells or specialize into any cell in the body, replacing damaged cells or potentially growing new organs. Organs grown from a patient’s own cells would eliminate the need for anti-rejection medication, reducing the risks associated with transplantation. Stem cells also show promise in treating diseases and genetic conditions. For example, manipulated bone marrow cells have halted the progression of a fatal brain disease in children, suggesting stem cell therapy is the future of medicine.
Targeted Cancer Therapies Improve Survival Rates
Traditional cancer treatments like chemotherapy and radiation often harm healthy cells alongside cancerous ones. Newer targeted therapies, however, selectively attack cancer cells without damaging healthy tissue. These therapies identify and kill cancer cells directly or interfere with processes that cause tumor growth. Over the past decade, the FDA has approved more than 25 new targeted therapy medicines. These drugs, including small-molecule and monoclonal antibodies, target specific functions that help cancer cells divide, grow, and spread, marking a significant advance in the fight against cancer.
Nanomedicine Left Science-Fiction Behind
Nanomedicine, long a staple of science fiction, is now a tangible reality focused on drug delivery. Instead of impossibly tiny robots, nanomedicine employs nanoparticles designed to target specific cells, delivering drugs directly to affected areas while avoiding healthy cells. This reduces the required drug amount and minimizes side effects. Nanotechnology-based drugs like Abraxane and Onivyde have already improved anti-rejection and cancer treatments. Ongoing research aims to further advance treatments for HIV and cancer, signaling a future with fewer side effects and greater drug effectiveness.
It Is Now Possible To Print Body Parts

The ability to fabricate body parts from raw materials is no longer confined to science fiction. Advanced 3D printing technology now allows for the creation of implantable body parts by combining cell types with polymers to produce living, functional tissues. While still in early development, this technology has achieved significant milestones. By 2020, researchers successfully printed and implanted bionic eyes, hearts, skin, ears, bones, ovaries, and antibacterial teeth in animals. As the technology matures, specialized 3D printers could recreate organs for human implantation, reducing the wait for transplants.
RNA Vaccines Took The Fight To The Virus

The rapid development of COVID-19 vaccines is a remarkable medical achievement, largely due to advancements in RNA vaccine technology. Unlike traditional vaccines that use an inactive virus, RNA vaccines deliver nucleic acid encoding the protein to trigger an immune response. The body then makes the protein needed to fight the virus. The COVID-19 vaccines are the first RNA vaccines to move beyond the testing phase and into widespread use. Their success paves the way for fighting viruses that have been difficult to combat in the past, marking RNA vaccines as one of the century’s most important medical advancements.
What do you think about these advancements? Leave your comment below!