We all enjoy a sweet treat now and then, but how much do we really know about where that sugar comes from and its impact on our world? The story of sugar is far from sweet, filled with controversy, deception, and significant consequences. It’s time to peel back the sugary coating and look at some unsettling truths the industry might prefer you didn’t know. Prepare to be surprised by these 10 not-so-sweet facts.
10. A Bitter History of Slavery
 Sugar’s rise to global popularity is deeply rooted in a dark and tragic past: the exploitation of slave labor. Originally a luxury spice for wealthy Europeans, sugarcane cultivation in the West Indies and Brazil, later expanding to a massive scale in the American colonies, became incredibly profitable. This ‘White Gold’ fueled economies but at a terrible human cost.
Sugar’s rise to global popularity is deeply rooted in a dark and tragic past: the exploitation of slave labor. Originally a luxury spice for wealthy Europeans, sugarcane cultivation in the West Indies and Brazil, later expanding to a massive scale in the American colonies, became incredibly profitable. This ‘White Gold’ fueled economies but at a terrible human cost.
The crop’s labor-intensive nature led to the horrific enslavement of countless individuals, including children. They toiled under brutal conditions in plantations and processing plants, particularly in places like Louisiana. Exhaustion and horrific accidents, such as losing limbs in machinery, were tragically common. Greed overshadowed humanity, allowing the sugar trade to thrive on the destruction of cultures and lives. That bag of sugar in your kitchen has a history far more complex than you might imagine.
9. Congressional Ties and Financial Schemes
 Sugar’s influence quickly extended into the halls of power. As early as 1816, the United States Congress imposed tariffs on imported sugar, a move that favored sugar produced by slave labor within the country, especially in states like Louisiana. This wasn’t just about trade; it was about bolstering an industry built on oppression.
Sugar’s influence quickly extended into the halls of power. As early as 1816, the United States Congress imposed tariffs on imported sugar, a move that favored sugar produced by slave labor within the country, especially in states like Louisiana. This wasn’t just about trade; it was about bolstering an industry built on oppression.
This era also saw the rise of dubious banking practices centered in Louisiana. These schemes allowed plantation owners to pledge their estates and enslaved people as assets to secure loans. This capital was then used to expand their operations and acquire more enslaved individuals. Banks bundled these assets, creating slave and mortgage-backed securities sold to investors, locally and internationally. When investors raised concerns about the ‘perishability’ of enslaved people, Louisiana even issued state bonds to guarantee these investments, further fueling the industry’s growth and the tragic expansion of slavery.
8. Modern-Day Forced Labor
 Shockingly, the ugly shadow of forced labor still darkens the sugar industry today. In places like the Dominican Republic, thousands of Haitians, often indebted and lacking identification, are lured by false promises of paid work. They end up in labor camps known as ‘bateyes’, working grueling 12-14 hour days harvesting sugarcane for meager wages, often paid in company scrip rather than actual currency.
Shockingly, the ugly shadow of forced labor still darkens the sugar industry today. In places like the Dominican Republic, thousands of Haitians, often indebted and lacking identification, are lured by false promises of paid work. They end up in labor camps known as ‘bateyes’, working grueling 12-14 hour days harvesting sugarcane for meager wages, often paid in company scrip rather than actual currency.
Traffickers often intercept these vulnerable individuals, selling them to farms. The products of this forced labor can unknowingly end up on supermarket shelves worldwide. While awareness is slowly growing, and initiatives like the UK’s Modern Slavery Act aim to combat these practices, the fight is far from over. Consumer choices can play a powerful role in demanding ethical sourcing.
7. A Legacy of Lies and Deception
 The sugar industry has a history of actively misleading the public. In the 1960s, the Sugar Research Foundation (SRF) funded research by Harvard scientists. Their findings, published in the prestigious New England Journal of Medicine in 1967, downplayed the role of sugar in heart disease and instead pointed the finger at fat and cholesterol. Crucially, the SRF’s funding and influence were not disclosed.
The sugar industry has a history of actively misleading the public. In the 1960s, the Sugar Research Foundation (SRF) funded research by Harvard scientists. Their findings, published in the prestigious New England Journal of Medicine in 1967, downplayed the role of sugar in heart disease and instead pointed the finger at fat and cholesterol. Crucially, the SRF’s funding and influence were not disclosed.
This carefully orchestrated review manipulated scientific discourse for decades, shaping public understanding and dietary guidelines. It allowed the industry to sidestep scrutiny while public health suffered. This strategic deception highlights how powerful industries can manipulate information to protect their interests, often at the expense of consumer well-being.
6. Sugar: A Hidden Poison?
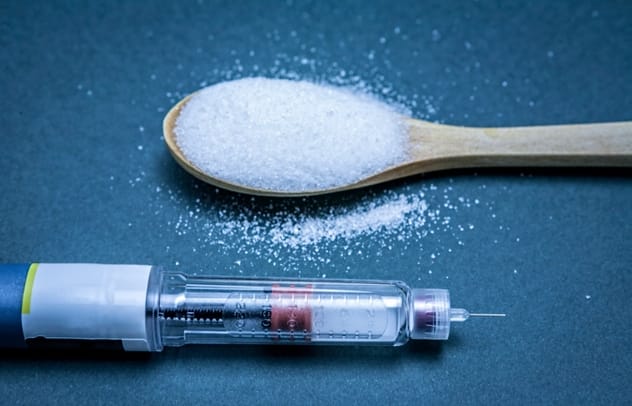 We often indulge in sugary treats, but the industry works hard to obscure the full extent of sugar’s impact on our health. While we associate sugar with pleasure, experts like Marion Nestle have pointed out how food company sponsorship can undermine public trust in nutrition science and lead to confusion about healthy eating.
We often indulge in sugary treats, but the industry works hard to obscure the full extent of sugar’s impact on our health. While we associate sugar with pleasure, experts like Marion Nestle have pointed out how food company sponsorship can undermine public trust in nutrition science and lead to confusion about healthy eating.
The reality is that excessive sugar consumption is linked to a host of health problems. It can promote fat storage in the liver, contribute to insulin resistance, lead to increased insulin production, and has even been implicated in promoting tumor growth. The sweet allure of sugar hides a potentially bitter truth about its effects on our bodies.
5. Profits Over Public Health
 The sugar industry’s commitment to its bottom line, even at the potential cost of public health, is starkly evident. When the World Health Organization (WHO) declared that sugar should constitute no more than 10 percent of a healthy diet, industry groups, including the Sugar Association, reportedly pressured the United States Congress to withdraw funding from the WHO unless the report was retracted.
The sugar industry’s commitment to its bottom line, even at the potential cost of public health, is starkly evident. When the World Health Organization (WHO) declared that sugar should constitute no more than 10 percent of a healthy diet, industry groups, including the Sugar Association, reportedly pressured the United States Congress to withdraw funding from the WHO unless the report was retracted.
This aggressive stance makes it clear: for some in the industry, profits and continued growth seem to take precedence over the health and safety of consumers. This raises serious questions about the ethics of an industry that appears to prioritize its financial interests above all else.
4. The Sneaky Truth About ‘Healthy’ Foods
 Sugar isn’t just in obvious culprits like desserts and sodas. It lurks in many foods marketed as ‘healthy’, ‘low-fat’, or ‘light’. When fat is removed from products like yogurt to make them ‘low-fat’, sugar is often added to compensate for the loss of flavor and texture. This means some ‘healthy’ options can have surprisingly high sugar content.
Sugar isn’t just in obvious culprits like desserts and sodas. It lurks in many foods marketed as ‘healthy’, ‘low-fat’, or ‘light’. When fat is removed from products like yogurt to make them ‘low-fat’, sugar is often added to compensate for the loss of flavor and texture. This means some ‘healthy’ options can have surprisingly high sugar content.
Beyond that, everyday items like ketchup, jarred spaghetti sauces, and barbecue sauce can be packed with sugar. Sports drinks, fruit juices, iced teas, so-called ‘vitamin’ waters, premade smoothies, and flavored coffees are also significant sources. Even cereals, granola, protein bars, and some canned soups and fruits contain more sugar than you might expect. This hidden sugar makes it easy to consume far more than recommended without even realizing it.
3. Damaging Our Climate
 The escalating global consumption of sugar also carries a heavy environmental toll. Traditional sugarcane farming methods often involve the use of nitrous oxide fertilizers. Nitrous oxide is an incredibly potent greenhouse gas, with a global warming potential around 300 times that of carbon dioxide. This contributes significantly to climate change.
The escalating global consumption of sugar also carries a heavy environmental toll. Traditional sugarcane farming methods often involve the use of nitrous oxide fertilizers. Nitrous oxide is an incredibly potent greenhouse gas, with a global warming potential around 300 times that of carbon dioxide. This contributes significantly to climate change.
While more sustainable farming practices are emerging, the industry’s overall impact remains a concern. Ironically, climate change itself, with rising temperatures, can negatively affect sugarcane ripening, potentially creating a feedback loop where the industry’s practices contribute to conditions that harm its own production. Hopefully, a shift towards more eco-conscious methods will gain momentum to mitigate this damage.
2. The Addictive Power of Sweetness
 The sugar industry benefits from a powerful, naturally occurring phenomenon: sugar’s addictive quality. Consuming sugar triggers the release of dopamine in the brain, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward. This creates cravings, encouraging us to seek out more sugary foods. Many processed foods high in sugar are specifically designed to be ‘hyperpalatable’, making them difficult to resist and easy to overconsume.
The sugar industry benefits from a powerful, naturally occurring phenomenon: sugar’s addictive quality. Consuming sugar triggers the release of dopamine in the brain, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward. This creates cravings, encouraging us to seek out more sugary foods. Many processed foods high in sugar are specifically designed to be ‘hyperpalatable’, making them difficult to resist and easy to overconsume.
Startling research in animals has even suggested that sugar can be more addictive than cocaine. Animals in these studies not only preferred sugar but also exhibited signs of withdrawal when it was removed. While human experiences are complex, the constant availability of sugar in our diets means many of us rarely experience true withdrawal, perpetuating a cycle of consumption that benefits the industry.
1. Miracle Fruit: The Suppressed Alternative?
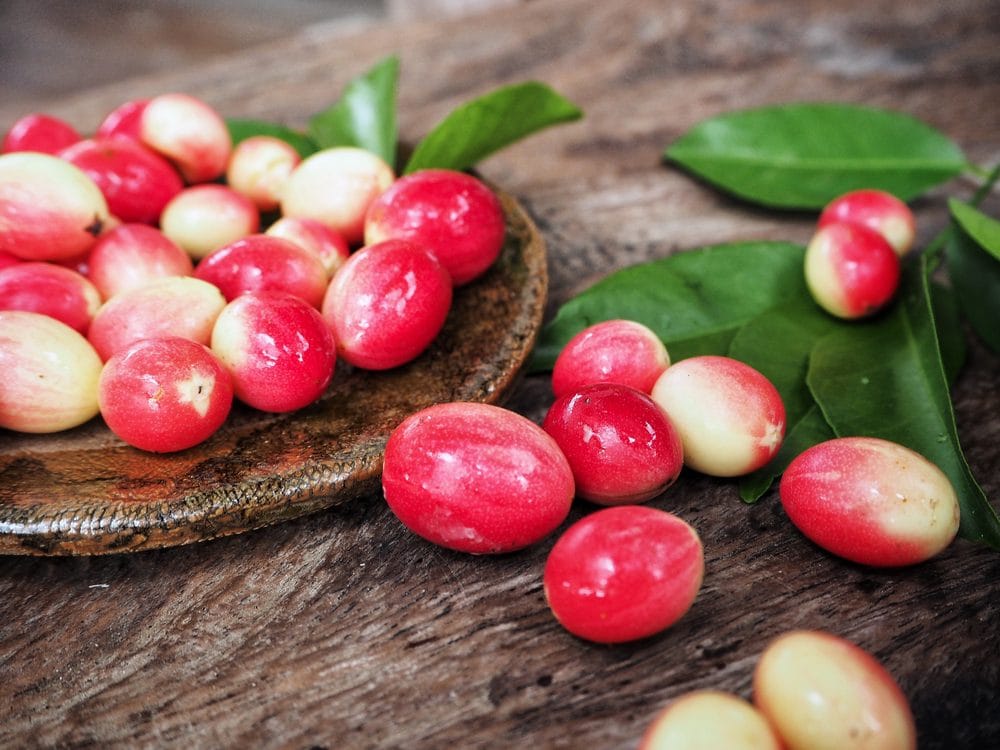 Have you ever heard of Miracle Fruit? This small berry contains a glycoprotein called miraculin, which has a fascinating effect: it makes sour foods taste incredibly sweet for several hours after consumption. Imagine eating a lemon as if it were a sweet orange! This natural, calorie-free alternative to sugar sounds like a game-changer, doesn’t it?
Have you ever heard of Miracle Fruit? This small berry contains a glycoprotein called miraculin, which has a fascinating effect: it makes sour foods taste incredibly sweet for several hours after consumption. Imagine eating a lemon as if it were a sweet orange! This natural, calorie-free alternative to sugar sounds like a game-changer, doesn’t it?
So, why isn’t it more widely known and used? The story goes that in 1977, efforts to commercialize miraculin were effectively halted by the FDA. Some allege this decision was influenced by lobbying from existing sugar and artificial sweetener industries, like the makers of aspartame, who saw miracle fruit as a threat to their market. Though it’s now more accessible, its journey highlights how powerful established industries can be in controlling the narrative around alternatives. Discovering and supporting such alternatives could be a step towards reducing reliance on the traditional sugar industry.
The sugar industry’s history and current practices are complex and, at times, deeply troubling. From its foundations in slave labor to modern-day health controversies and environmental impacts, there’s more to that spoonful of sugar than meets the eye. Being an informed consumer is the first step towards making choices that align with your health and values. The power to change lies in awareness and conscious decisions.
What are your thoughts on these facts about the sugar industry? Share your comments below!










